Here’s the structure of normal skin and what changes it goes through.
Cross section of human skin
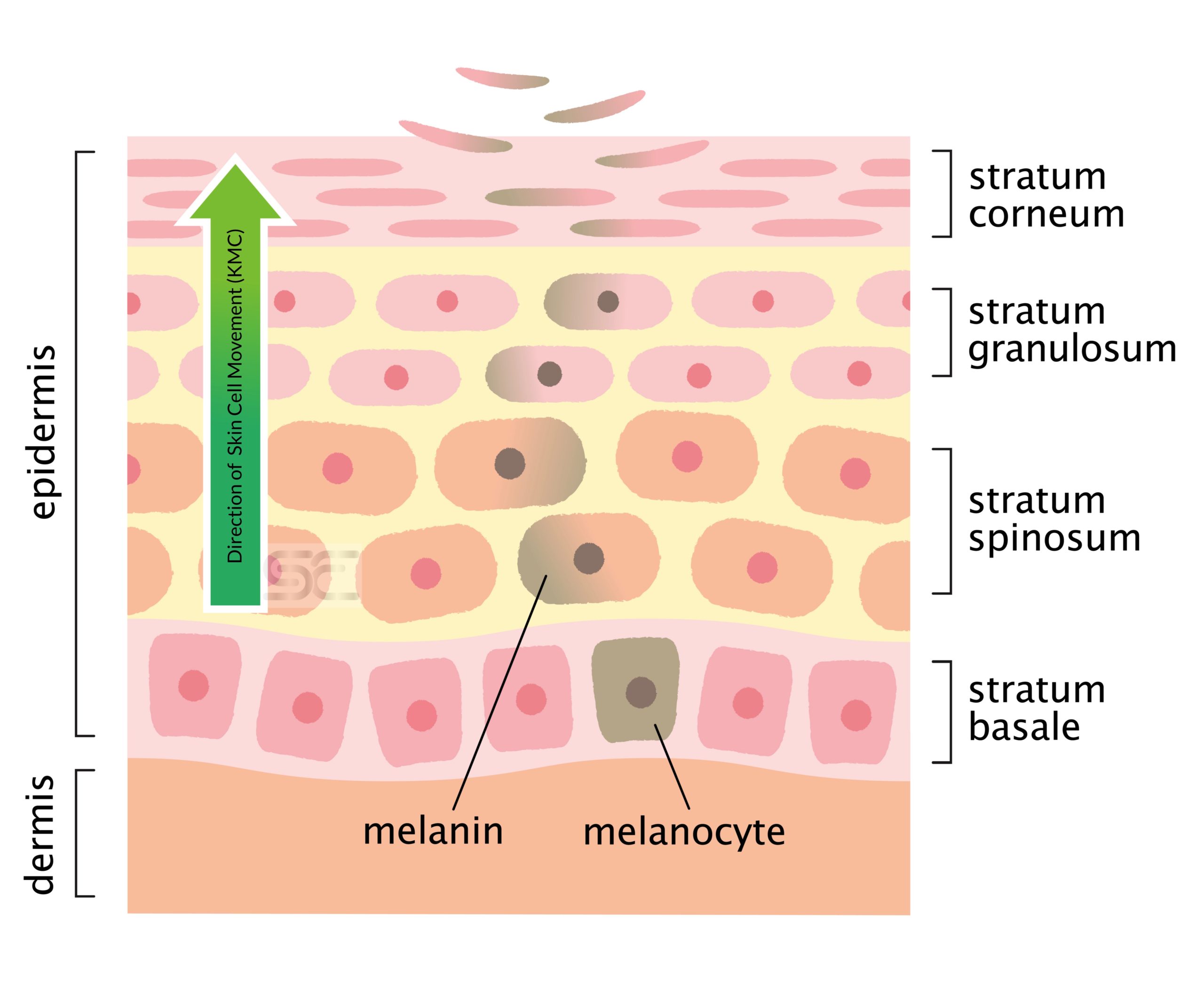
There are five layers of cells in the epidermis (top layer) of the skin. Each new skin cell (keratinocyte) is made at the bottom of these layers in the Basement Membrane (Stratum Basale). Once made, it is slowly pushed up to the top (Stratum Corneum). As each layer of cells goes up it picks up melanin (pigment/colour), loses some of its fluid content, gets tightly packed together and hardens. This process takes 4 weeks in the youthful skin and is called the cell turnover or keratinocyte maturation cycle (KMC).
Once the cells reach the top, the cells are dead and appear as a thickened layer protecting the inner layers from the environment. Eventually, the connections between the top layer and the next layer breaks and the surface layer are sloughed off as we rub or wash our skin.
In summary, a cell is born, matures, dies and is shed off in about 4 weeks.
Young skin is very good at replacing and repairing damaged skin. By damage, I mean minor injuries, acne, chicken pox and effects of the sun such as sunburns.
How Ageing affects Skin Cells
With ageing, this process slows down, and the cell turnover can take as long as 8 weeks.
Firstly, the basal layer makes less new cells and this leads to less shedding of the dead cells. Next, the layer at the top gets thicker leading to the texture of the skin becoming rough and uneven. The movement of cells slows down so that, by the time the cells reach the top they can be dull, dehydrated and sluggish. This can give the appearance of poor texture, enlarged or blocked pores and uneven pigmentation.
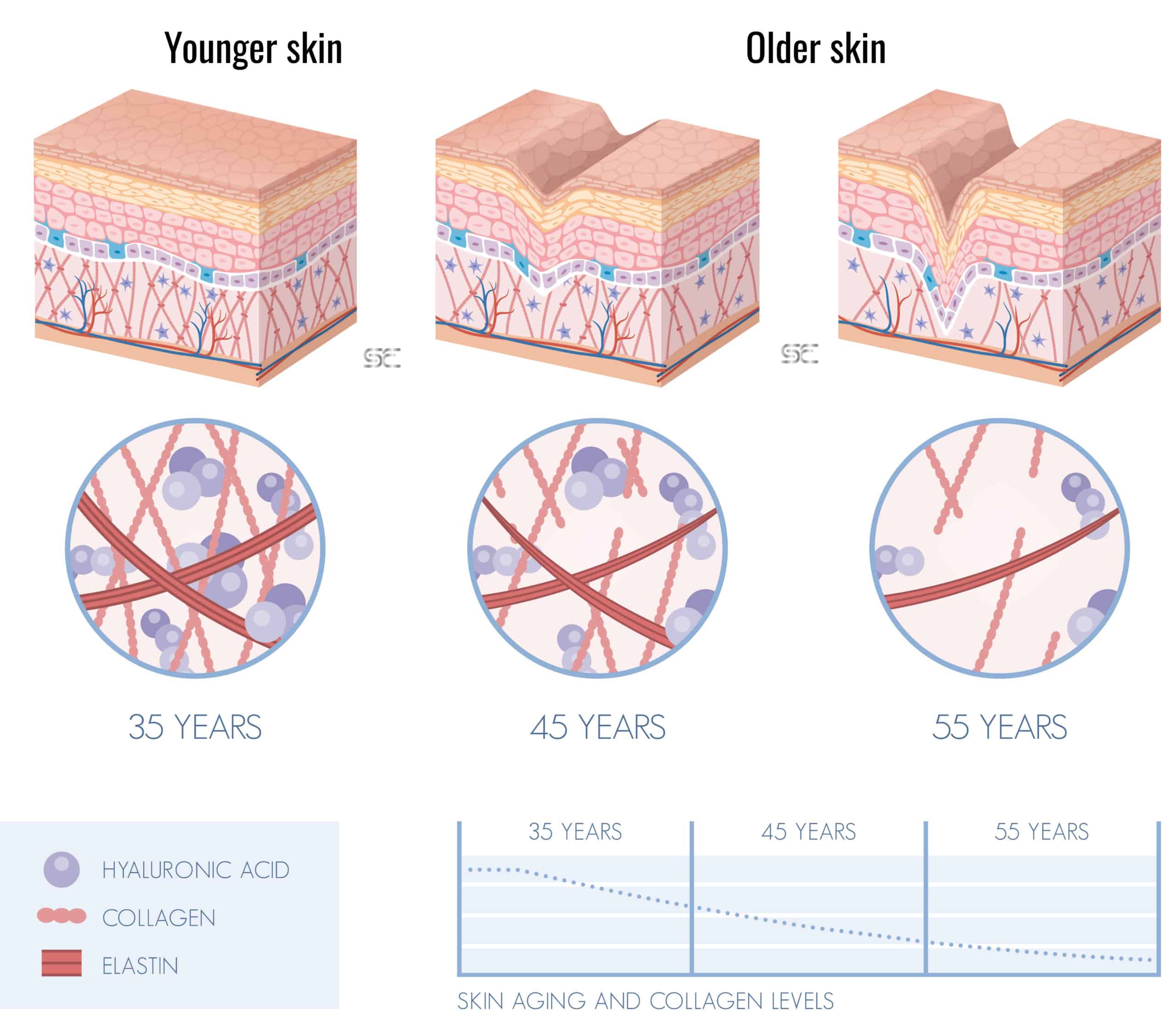
Secondly, with ageing, the deeper layer or dermis which normally provides support produces less collagen and elastin. This leads to reduced support for the epidermis. Folds start to appear on the surface appearing as lines and wrinkles.
Most importantly, the thickened top layer prevents absorption of active skincare ingredients to enter the dermis. Consequently, skincare products become ineffective.
Did you know that the slowing down of the skin cell cycle can start as early as 25 years? The skin is much slower at rejuvenating and repairing itself after this age.
Comparison of younger versus older skin
What are the Benefits of Exfoliation?
There are two main benefits. Firstly, when you exfoliate you remove the top layer of dead skin. Consequently, the removal of the top layer stimulates the skin to speed up its new cell production. Therefore, exfoliation doesn’t just improve resilience and radiance. But it also encourages the skin to behave like it did when it was younger! Circulation improves, promoting many health benefits and vitality to the skin.
Types of Exfoliation
You can exfoliate the skin mechanically, chemically or a combination of both.
Why you should exfoliate your skin regularly?
Mechanical (Physical) Exfoliation
You physically remove the dead skin using a rough product to buff away dead skin. This gives instant polishing effects to the skin. In Medical grade skincare, unlike high street beauty products, the exfoliants are smooth spherical crystals. The crystals are able to powerfully remove the dead skin without causing any microscopic damage to the surface of the skin. As a rule of thumb, these products always include hydrators and healthy lipids to support the skin.
You can either opt for daily exfoliants or potent exfoliants once or twice-weekly ones. If you have sensitive skin, then gentler exfoliants are preferred in the winter months.
Chemical Exfoliation
This involves using acids to lower the pH of the skin. The skin’s normal pH is acidic between 4.5 and 6.2. This is due to the thin layer of acid mantle on the skin. The acid mantle is made when sweat mixes with the sebum produced in the skin and forms a protective barrier against bacteria, viruses, etc. When a more acidic solution is applied to the skin, the dead skin cells at the top comes off the surface as connections between cells are broken.
Some types of chemical exfoliation are safe to do at home by yourself while others need to be carried out by a professional (chemical peels). Common acids used in chemical exfoliation are alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs).
Alpha-hydroxy acids
These acids are hydrophilic (love water) and remove water bonds present between cells at the top layer of skin. Common examples are lactic acid, mandelic acid, and glycolic acid. AHAs at increasing percentages are capable of not only exfoliating but also increase collagen and elastin production in the deeper layers.
Beta-hydroxy acids
These acids are lipophilic (love oil) and penetrate deeper into pores to break down oil and sebum, hence are great for acne and blocked pores. They are usually used in combination with other ingredients to get more potent benefits. A common example is salicylic acid.
Fruit enzymes
When fruit enzymes are used to exfoliate, this creates an invisible exfoliation. Occasionally fruit enzymes are combined with chemical exfoliants to provide a cumulative effect.
Third generation ‘Bionic’ acids developed by NeoStrataâ include lactobionic acid, maltabionic acid and gluconolactone. They can gently exfoliate without irritation.
Once the dead skin on the surface is removed, the skin becomes more receptive to take active ingredients. Antioxidants, vitamins, peptides, and hydrating agents can target the active skin cells to rejuvenate and repair the skin.
Although exfoliation with any method gives great benefits, it is important to choose the right exfoliant for each skin type. For example, over washing blemish prone skin can stimulate excess sebum production and aggravate acne. This is because when the skin surface is dry the skin responds by producing more sebum.
Chemical Peels are intense exfoliation carried out under controlled conditions.
Good examples of daily exfoliants
ZO®Skin Health Exfoliating Cleanser (chemical and mechanical)
ZO® Skin Health Exfoliating Polish (mechanical)
Obagi360®Exfoliating cleanser (mechanical)
Obagi Nu-Derm® Exfoderm (chemical)
AlumierMD Bright & Clear Solution (chemical)
AlumierMD AHA Renewal Serum (chemical)
AlumierMD Acne clarifying cleanser (chemical)
NeoStrata® cleansers (chemical)
Examples of exfoliants used weekly or twice weekly include:
AlumierMD Lotus scrub (mechanical)
AlumierMD Enzymatic Peel (chemical)
ZO® Skin Health Dual Action Scrub (Chemical and mechanical)
ZO® Skin Health Enzymatic Peel (chemical)
ZO® Skin Health Exfoliation Accelerator (chemical)
In summary, you need to exfoliate all through the year, but the type of product used should be adjusted to your skin type. It may be necessary to use extra hydration during the harsh winter climate. However, sun protection should be used all year round.


Recent Comments