Did you realise that safeguarding your skin from the sun is a must during every moment of daylight, regardless of the season? Sunscreen isn’t solely reserved for tropical getaways—it’s an everyday essential. While many apply sunscreen on sunny days to dodge sunburns, it’s crucial to understand that sunburn stems from UVB rays, which only represent a fraction of the ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earth’s surface.
The sun’s radiation encompasses various forms beyond UVB, including UVA, visible light, and Infrared-A, persisting throughout the year and throughout the day. These components inflict significant harm on our skin.
Renowned dermatologist Dr. Zein Obagi underscores the role of sun exposure in inducing chronic inflammation, disrupting cellular functions, and compromising the skin’s immunity, particularly its ability to self-repair. The repercussions of this damage may emerge a decade or more following initial exposure.
While ageing is an inevitable biological process, external influences can hasten its pace. Factors like sun exposure and lifestyle choices significantly contribute to premature ageing.
In the UK, skin cancer stands as the most prevalent form of cancer. The British Skin Foundation emphasizes that UV protection is pivotal in warding off these malignancies.
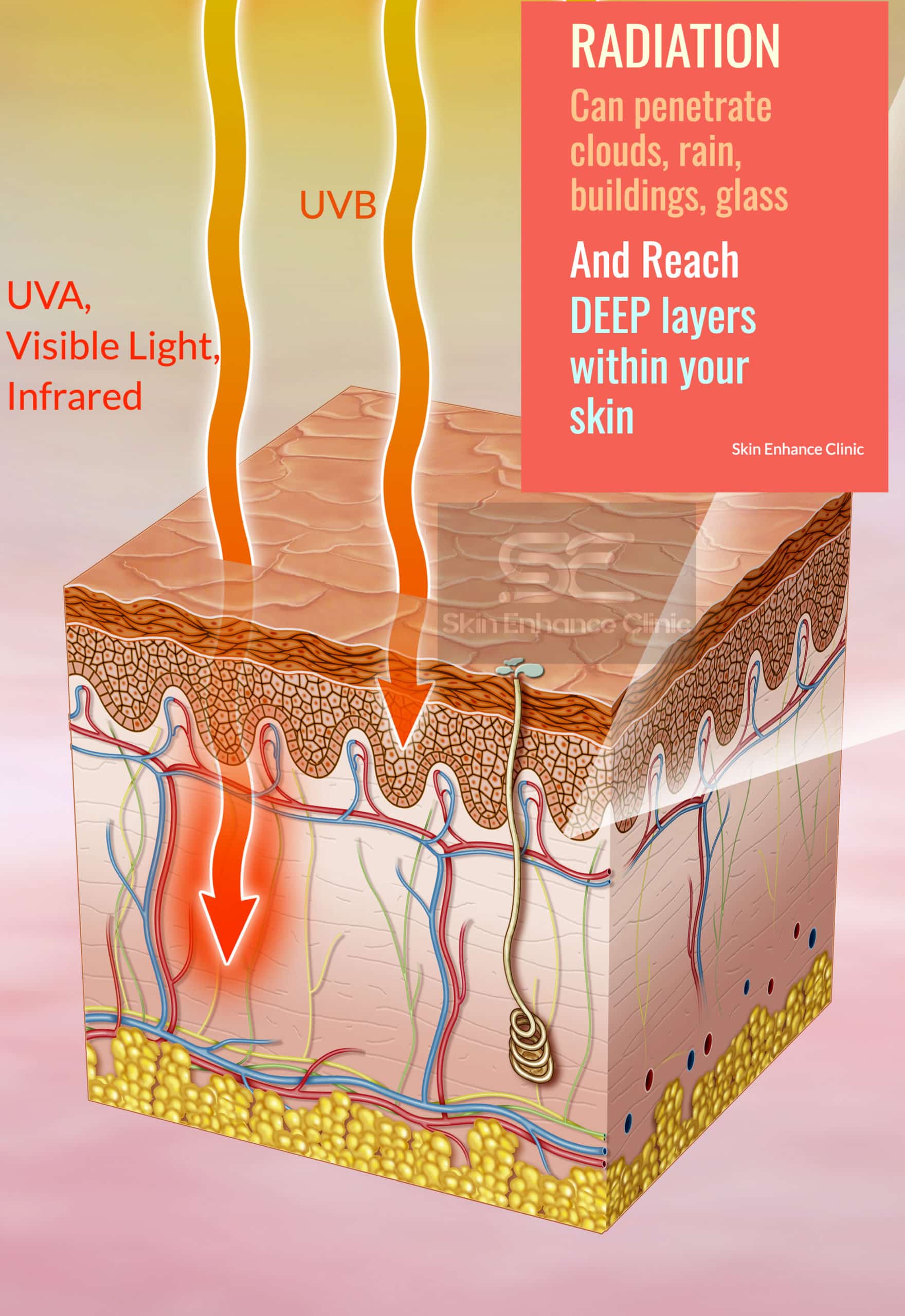
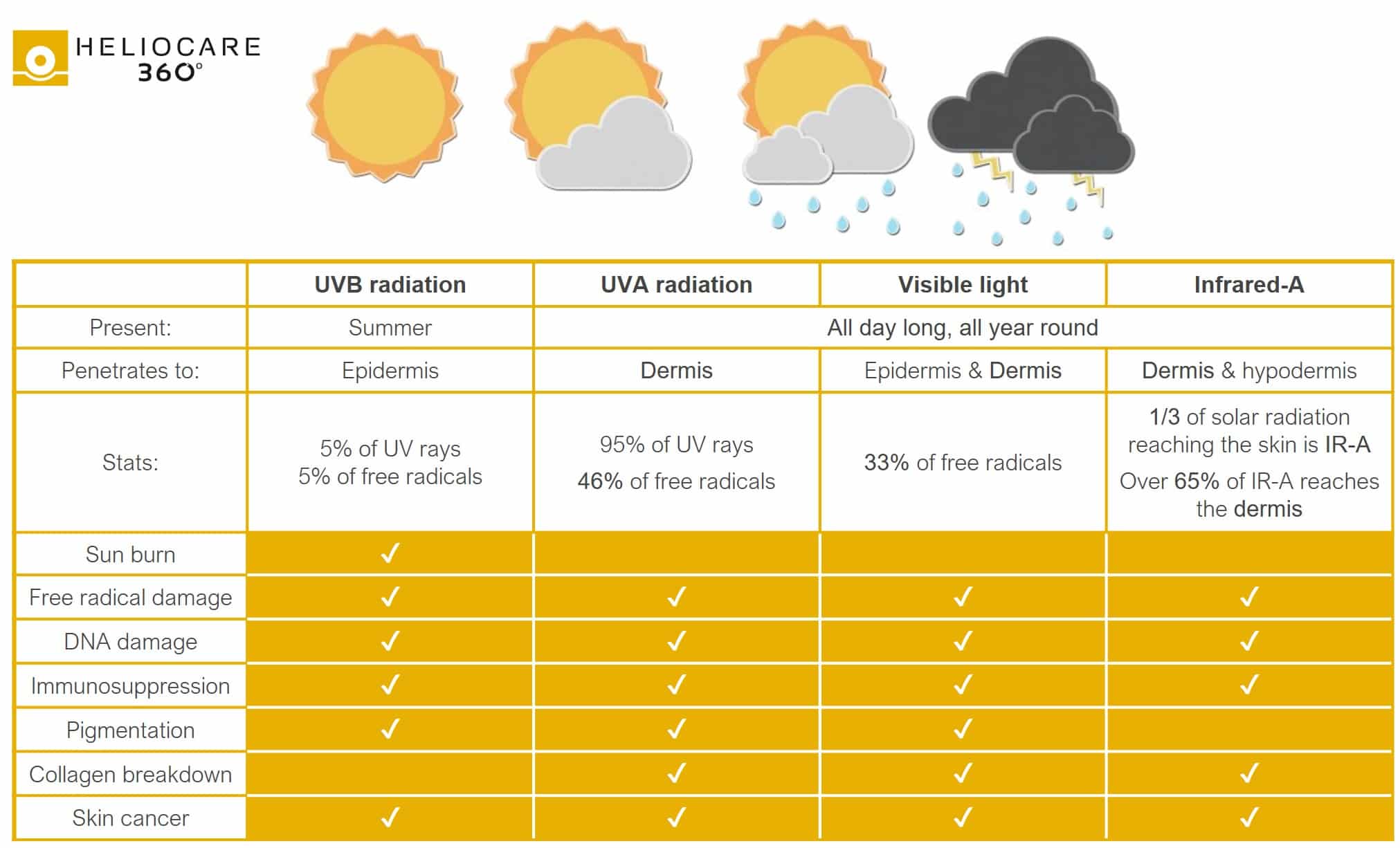
Below is an excellent illustration of UV radiation damage provided by Heliocare 360°.
Layers of the skin
- Epidermis
This is the outermost thin layer of the skin providing a barrier function.
- Dermis
The dermis is the deeper, thicker layer which provides structure and support to the skin. It is the layer that contains collagen and elastin that provides youth and hydration to our skin.
- Hypodermis
Hypodermis is the layer that contains fat and provides insulation and padding for the body.
Understanding the Impact of UV Radiation on Your Skin
In the illustration provided, it’s evident that UVB radiation constitutes a mere 5% of the total radiation. Limited to the epidermis, UVB damage encompasses issues such as free radical damage, pigmentation, and sunburn. It’s essential to note that while SPF shields against UVB, it doesn’t safeguard against other forms of radiation discussed below, making SPF alone an insufficient metric.
On the flip side, UVA radiation accounts for the remaining 95% and is omnipresent, penetrating through clouds, buildings, and even glass. Unlike UVB, UVA can delve into the dermis, inflicting long-term harm such as DNA damage, pigmentation, and collagen degradation, hastening skin ageing. Exposure to UVA isn’t confined to outdoor settings; it permeates through environments like cars, trains, and aeroplanes.
Moreover, visible light and Infrared-A, akin to UVA, persist throughout the day, regardless of the season, posing threats to the dermis and hypodermis. High Energy Visible Light, a subset of visible light, extends beyond solar emission, emanating from sources like fluorescent and LED lighting, as well as everyday devices such as smartphones, computers, and tablets.
Understanding Free Radical Damage: Unveiling its Causes and Effects
Free radical damage, triggered by various forms of radiation, is a phenomenon worth delving into. But what exactly are free radicals, and how do they wreak havoc?
In essence, free radicals are unstable molecules lacking electrons. In their quest to regain stability, these highly reactive entities plunder electrons from within cells, leading to cellular havoc. They’re capable of inflicting damage on vital cellular components such as DNA, proteins, and lipid structures. Fortunately, our body’s defence mechanism comprises antioxidants, which step in to replenish missing electrons and stabilize free radicals, thus safeguarding our cells.
While radiation serves as a prominent source of free radicals, other culprits include routine metabolic reactions, along with lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption, tobacco use, and exposure to pollutants. The eventual outcome of this cellular assault is cell demise. While cell death is a natural occurrence, an imbalance favouring free radicals can precipitate premature ageing.
Is Consuming Antioxidant-Rich Foods Sufficient to Shield Your Skin from Free Radical Damage?
While foods like blueberries and broccoli boast high antioxidant content, the body primarily allocates these nutrients to vital organs, resulting in inadequate levels reaching the skin’s surface.
Hence, to ensure optimal protection against free radical damage and maintain healthy, radiant skin, it’s imperative to utilise specialised antioxidant skincare products directly on the skin.
Navigating Snowy Environments: Understanding Increased UV Exposure
With the ski season on the horizon, it’s crucial to recognise the heightened UV exposure posed by snowy conditions. At higher altitudes, the atmosphere offers less filtration of radiation, amplifying its impact. The reflective nature of snow covering all surfaces further intensifies this effect. Additionally, unlike sunny days where individuals seek refuge in the shade, most people spend extended periods skiing outdoors, prolonging their exposure to harmful UV rays.
Understanding Physical and Chemical Sunscreens: What Sets Them Apart?
Sunscreens fall into two main categories: Physical and Chemical, distinguished by their ingredients and mechanisms of action. Physical sunscreens feature large molecules that linger on the skin’s surface, deflecting and scattering ultraviolet radiation rather than absorbing it. As a result, they often provide sufficient protection with a single daily application. Key UV filters in physical sunscreens include zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, offering immediate protection upon application.
On the other hand, chemical filters comprise smaller molecules that penetrate the skin. These filters function by absorbing UV radiation, converting it into heat energy, and dispersing it. Consequently, their concentration diminishes on the skin over time, necessitating reapplication every two hours to maintain effectiveness. It’s crucial to apply chemical sunscreens at least 20 minutes before sun exposure for optimal absorption. Below, you’ll find a selection of sunscreens available at Skin Enhance and Wellness.
In the following video, I discuss what I recommend to all my patients attending for a consultation.
ZO® Skin Health Sunscreen

Colorescience® Sunscreen
All Colorescience products are mineral-based, infused with antioxidants and gentle enough for all ages and skin types.

Obagi® Medical Sunscreen

AlumierMD Sunscreen
AlumierMD only uses physical filters in all their sunscreens. They avoid chemical filters in their sunscreens stating that chemical filters can potentially be changed by UV radiation and may release free radicals of their own which can cause harm to the surrounding tissue.

Understanding SPF and Star Ratings on Sunscreens
When selecting a sunscreen, ensure it provides adequate protection against the full spectrum of radiation. Relying solely on the SPF number is insufficient, as it primarily indicates UVB protection, while the star rating correlates with UVA protection. Cosmetic products labelled with SPF may not offer the comprehensive protection required for optimal skin health.


Recent Comments